Whole-genome sequencing in a family with twin boys with autism and intellectual disability suggests multimodal polygenic risk
Abstract
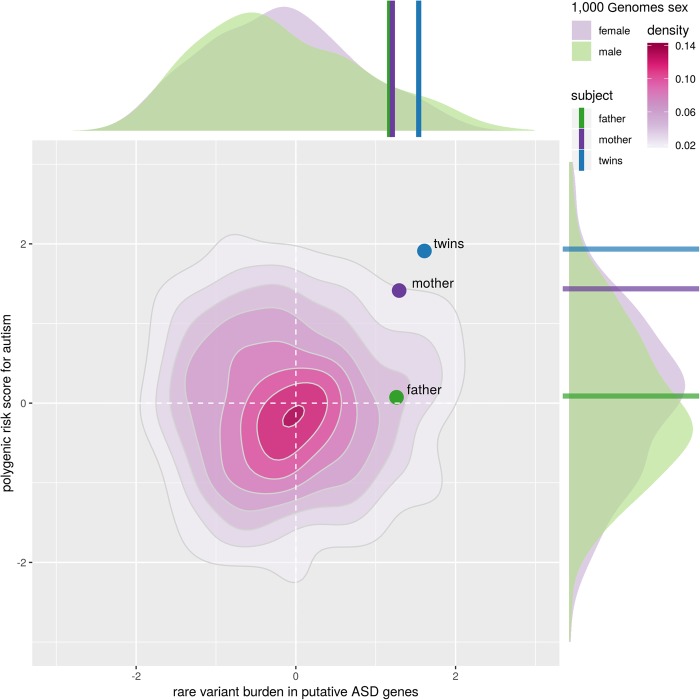
Over the past decade, a focus on de novo mutations has rapidly accelerated gene discovery in autism spectrum disorder (ASD), intellectual disability (ID), and other neurodevelopmental disorders (NDDs). However, recent studies suggest that only a minority of cases are attributable to de novo mutations, and instead these disorders often result from an accumulation of various forms of genetic risk. Consequently, we adopted an inclusive approach to investigate the genetic risk contributing to a case of male monozygotic twins with ASD and ID. At the time of the study, the probands were 7 yr old and largely nonverbal. Medical records indicated a history of motor delays, sleep difficulties, and significant cognitive deficits. Through whole-genome sequencing of the probands and their parents, we uncovered elevated common polygenic risk, a coding de novo point mutation in CENPE, an ultra-rare homozygous regulatory variant in ANK3, inherited rare variants in NRXN3, and a maternally inherited X-linked deletion situated in a noncoding regulatory region between ZNF81 and ZNF182. Although each of these genes has been directly or indirectly associated with NDDs, evidence suggests that no single variant adequately explains the probands’ phenotype. Instead, we propose that the probands’ condition is due to the confluence of multiple rare variants in the context of a high-risk genetic background. This case emphasizes the multifactorial nature of genetic risk underlying most instances of NDDs and aligns with the “female protective model” of ASD.